Filing taxes in the U.S. as a nonresident alien can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. If you earned income while in the United States and aren’t a citizen or green card holder, you may need to file Form 1040NR. In this guide, we’ll break down who needs to file, what you’ll need, and how to complete your 1040NR easily and accurately.
What is Form 1040NR?
Form 1040NR, officially called the U.S. Nonresident Alien Income Tax Return, is used by individuals who are not U.S. citizens or permanent residents but still earned income from U.S. sources. Whether you received wages, scholarships, investment income, or ran a small business in the U.S., this form may apply to you.
Who Needs to File Form 1040NR?
You are generally required to file Form 1040NR if:
- You earned income from a U.S. business, employer, or investment.
- You had U.S. source income and not enough tax was withheld.
- You are claiming a refund for taxes withheld.
- You’re a student, teacher, trainee, or researcher on an F, J, M, or Q visa and earned taxable income.
- You are a dependent or spouse of a visa holder with taxable income.
Common examples:
F-1 students with scholarships, J-1 researchers earning stipends, or H-1B visa holders with partial-year residency.
What Documents Do You Need?
Before you start filling out Form 1040NR, gather the following:
- Passport and visa details
- Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN)
- Forms W-2, 1042-S, and/or 1099 for income received
- Records of deductions, treaty benefits, or exemptions
- Form 8843 (if you’re an international student, teacher, or trainee)
Step-by-Step: How to Complete Form 1040NR
1. Fill Out Your Personal Information
Provide your name, current address, visa type, and tax ID. You’ll also indicate your residency status and type of income.
2. Report Your U.S. Source Income
List your wages, salaries, scholarships, dividends, and any other U.S. income sources. Only U.S.-earned income is taxable for nonresidents.
3. Apply for Tax Treaty Benefits (If Available)
Check if your home country has a tax treaty with the U.S. Tax treaties can reduce or eliminate your U.S. tax obligations for certain types of income.
4. Calculate Taxes and Refunds
Use the IRS instructions to calculate your total tax liability. If you paid more taxes than necessary, you can claim a refund.
5. Attach Required Forms
Attach any necessary documents like W-2s, 1042-S forms, and Form 8843 if you are a student or teacher on a qualifying visa.
6. File On Time
- April 15: If you earned wages
- June 15: If you didn’t earn wages
You can file by mail or through IRS-approved e-filing services for nonresidents.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Filing Form 1040 instead of 1040NR.
- Missing treaty exemptions you’re eligible for.
- Forgetting to sign the form or attach required documents.
- Filing after the deadline.
Tip: Always double-check the IRS mailing address or e-filing options to ensure your return gets processed correctly.
Of course!
You’re asking me to explain Form 1040-NR line-by-line, with simple examples — so anyone (even a first-timer) can understand how to fill it.
Here’s the breakdown:
How to Fill Out Form 1040-NR Line-by-Line (with Examples)
Top Section: Basic Information
| Field | What to Fill | Example |
|---|---|---|
| First Name, Middle Initial, Last Name | Your full legal name | Ali Khan |
| Identifying Number | SSN or ITIN (if you have it) | 123-45-6789 |
| Home Address | Your U.S. address (or foreign address if you live abroad) | 1234 Elm Street, Apt 5B |
| City, State, ZIP Code | City, State, and ZIP | New York, NY, 10001 |
| Foreign Address (If Applicable) | Country, province, postal code | Pakistan, Punjab, 54000 |
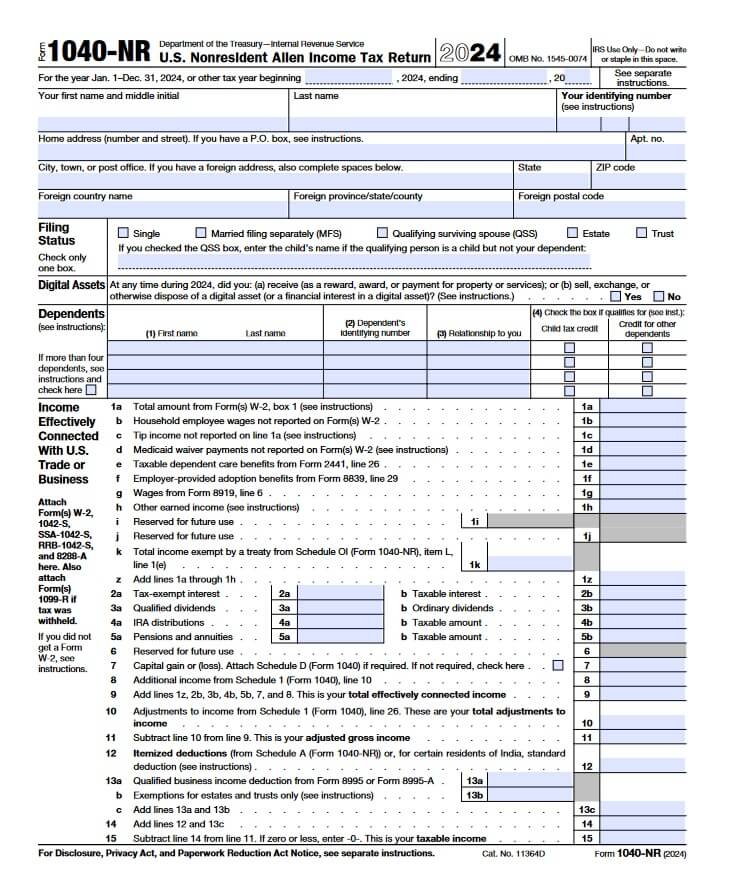
Filing Status:
☑ Choose only one:
| Options | Example |
|---|---|
| Single | Most nonresidents are Single |
| Married filing separately (MFS) | Only if married |
| Qualifying surviving spouse (QSS) | Rare for nonresidents (widow/widower cases) |
✅ Example: Ali is Single → He checks Single.
Digital Assets Question:
“At any time during 2024, did you buy, sell, or earn any crypto or digital asset?”
☑ Check Yes or No.
✅ Example:
Ali did not buy or sell Bitcoin → Check No.
Dependents:
- List children or others you financially support.
- Include their name, ITIN, relationship.
✅ Example:
Ali has no dependents → Leave blank.
Income Section (Effectively Connected Income)
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1a | Wages from Form W-2 | Ali earned $25,000 |
| 1b | Household employee wages (rare) | (Usually blank) |
| 1c | Tip income | Ali earned $1,000 in tips |
| 1h | Other earned income (consulting, freelancing) | Ali did a freelance project: $2,000 |
| 1k | Income exempt by treaty | Pakistan has no exemption for wages — leave blank |
➡️ Line 1z: Add 1a + 1c + 1h
✅ Total = $25,000 + $1,000 + $2,000 = $28,000
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 2a | Tax-exempt interest | (Usually blank) |
| 2b | Taxable interest (bank savings) | Earned $50 interest |
| 3a/3b | Dividends | Ali owns no stocks → blank |
| 4a/4b | IRA distributions | No retirement plan → blank |
| 5a/5b | Pension income | No pension → blank |
| 7 | Capital gains (stocks, real estate) | Sold some U.S. stocks, $500 profit |
➡️ Line 9:
Add: 28,000 + 50 + 500 = $28,550
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Adjustments (student loan interest, moving expenses for athletes) | None |
| 11 | Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) = Line 9 – Line 10 | $28,550 |
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Itemized or Standard Deduction | Indian citizens only standard deduction; otherwise itemized if eligible |
| 13 | QBI Deduction (self-employed only) | Ali is not self-employed → none |
➡️ Line 15:
Taxable Income = AGI – Deductions
✅ Example: $28,550 – $0 = $28,550
Tax and Credits Section
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 16 | Calculate tax from tax tables (based on $28,550) | ~$3,217 |
| 19 | Child Tax Credit | None |
| 20 | Other credits (education, foreign tax paid) | None |
➡️ Line 22 = Line 18 – Line 21
✅ Example: $3,217
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 23 | Income Not Effectively Connected (like dividends, royalties) | No NEC income |
| 24 | Total Tax Owed | $3,217 |
Payments Section
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 25a | Federal tax withheld (from W-2) | $4,000 withheld |
| 25g | Taxes withheld shown on 1042-S | $0 |
➡️ Line 33:
Total Payments = $4,000
Refund Section
✅ Refund = Line 33 – Line 24 = $4,000 – $3,217 = $783 refund.
| Field | Fill |
|---|---|
| 35a | Amount to refund = $783 |
| Bank details | Fill for direct deposit (Routing # and Account #) |
Amount You Owe
| Line | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 37 | If you owe more tax than you paid, this is the amount owed. | (Ali is getting a refund, so 0) |
Final Steps
✅ Sign and Date the return.
✅ If you use a tax preparer (CPA), they fill the “Paid Preparer Use Only” section.
✅ Attach W-2 and other forms (if needed).
Quick Summary of Ali’s Example:
| Wages + tips + freelance | $28,000 |
| Bank interest | $50 |
| Capital gains | $500 |
| Total income | $28,550 |
| Tax owed | $3,217 |
| Tax already withheld | $4,000 |
| Refund | $783 |





